以太坊源码分析:fetcher模块和区块传播
刘艳琴
发表于 2022-12-21 01:53:48
235
0
0
当前代码是以太坊Release 1.8,如果版本不同,代码上可能存在差异。
总体过程和传播策略9 v5 U: s2 d+ e# Q7 \8 K% F$ L: S
本节从宏观角度介绍,节点产生区块后,为了传播给远端节点做了啥,远端节点收到区块后又做了什么,每个节点都连接了很多Peer,它传播的策略是什么样的?
总体流程和策略可以总结为,传播给远端Peer节点,Peer验证区块无误后,加入到本地区块链,继续传播新区块信息。具体过程如下。0 s) _: K" k# h; R0 C4 _
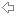
先看总体过程。产生区块后,miner模块会发布一个事件NewMinedBlockEvent,订阅事件的协程收到事件后,就会把新区块的消息,广播给它所有的peer,peer收到消息后,会交给自己的fetcher模块处理,fetcher进行基本的验证后,区块没问题,发现这个区块就是本地链需要的下一个区块,则交给blockChain进一步进行完整的验证,这个过程会执行区块所有的交易,无误后把区块加入到本地链,写入数据库,这个过程就是下面的流程图,图1。
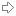
总体流程图,能看到有个分叉,是因为节点传播新区块是有策略的。它的传播策略为:
假如节点连接了N个Peer,它只向Peer列表的sqrt(N)个Peer广播完整的区块消息。向所有的Peer广播只包含区块Hash的消息。
策略图的效果如图2,红色节点将区块传播给黄色节点:
# M, q; q4 W: l
* l/ J N0 ?, x0 Q# i
收到区块Hash的节点,需要从发送给它消息的Peer那里获取对应的完整区块,获取区块后就会按照图1的流程,加入到fetcher队列,最终插入本地区块链后,将区块的Hash值广播给和它相连,但还不知道这个区块的Peer。非产生区块节点的策略图,如图3,黄色节点将区块Hash传播给青色节点:% P) U3 I1 s0 }' Q8 u6 e
: F( p0 R# d8 I" F' R3 b
至此,可以看出以太坊采用以石击水的方式,像水纹一样,层层扩散新产生的区块。
Fetcher模块是干啥的2 A6 B4 d) c( ]+ @ [' e0 v l( ]
fetcher模块的功能,就是收集其他Peer通知它的区块信息:1)完整的区块2)区块Hash消息。根据通知的消息,获取完整的区块,然后传递给eth模块把区块插入区块链。6 W6 J; I7 P4 E1 Z7 F0 ]
如果是完整区块,就可以传递给eth插入区块,如果只有区块Hash,则需要从其他的Peer获取此完整的区块,然后再传递给eth插入区块) R4 a7 Z1 m7 b5 |1 b
) d1 g# L2 Q5 Z0 Q% N
源码解读: q- T( {) |+ q; H' | Y* p- \
本节介绍区块传播和处理的细节东西,方式仍然是先用图解释流程,再是代码流程。$ A" [+ x* d% l- q
产块节点的传播新区块5 S% d! n% ~# O
节点产生区块后,广播的流程可以表示为图4:
发布事件事件处理函数选择要广播完整的Peer,然后将区块加入到它们的队列事件处理函数把区块Hash添加到所有Peer的另外一个通知队列每个Peer的广播处理函数,会遍历它的待广播区块队列和通知队列,把数据封装成消息,调用P2P接口发送出去
2 b8 V; `$ F! _
+ d, d* i) o9 J9 r
再看下代码上的细节。6 F4 s; A1 R/ W5 G: L5 `- H Z4 d
worker.wait()函数发布事件NewMinedBlockEvent。ProtocolManager.minedBroadcastLoop()是事件处理函数。它调用了2次pm.BroadcastBlock()。
// Mined broadcast loop
func (pm *ProtocolManager) minedBroadcastLoop() {- B+ j* H9 q( Z( k* Z3 ~
// automatically stops if unsubscribe& h: v( R. d) @* A
for obj := range pm.minedBlockSub.Chan() {4 v" c9 p5 g/ B) c7 E# P8 ^$ {
switch ev := obj.Data.(type) {
case core.NewMinedBlockEvent:
pm.BroadcastBlock(ev.Block, true) // First propagate block to peers
pm.BroadcastBlock(ev.Block, false) // Only then announce to the rest
}2 {1 m! \* H/ ^( p( N4 f q. x
}
}+ Z7 m7 R2 K- `, B4 |
pm.BroadcastBlock()的入参propagate为真时,向部分Peer广播完整的区块,调用peer.AsyncSendNewBlock(),否则向所有Peer广播区块头,调用peer.AsyncSendNewBlockHash(),这2个函数就是把数据放入队列,此处不再放代码。7 ^1 ]6 s) @2 Y s7 b1 j7 W
// BroadcastBlock will either propagate a block to a subset of it's peers, or8 ^+ | p: y5 u
// will only announce it's availability (depending what's requested).' g$ [+ I8 x0 x0 n$ f: `
func (pm *ProtocolManager) BroadcastBlock(block *types.Block, propagate bool) {" ?; t: a7 B |3 c! F: l# h+ {! ?
hash := block.Hash()
peers := pm.peers.PeersWithoutBlock(hash)8 s2 a1 x0 G6 S7 r7 z, @7 l
// If propagation is requested, send to a subset of the peer6 A5 c+ g0 t. Z% T. N
// 这种情况,要把区块广播给部分peer
if propagate {
// Calculate the TD of the block (it's not imported yet, so block.Td is not valid)* _" H6 t: _/ i+ o4 y4 r/ w
// 计算新的总难度
var td *big.Int
if parent := pm.blockchain.GetBlock(block.ParentHash(), block.NumberU64()-1); parent != nil {% @, n! \8 c2 N9 c+ M9 a
td = new(big.Int).Add(block.Difficulty(), pm.blockchain.GetTd(block.ParentHash(), block.NumberU64()-1))' F4 I! G ^6 M2 F5 i4 y# f
} else {
log.Error("Propagating dangling block", "number", block.Number(), "hash", hash)
return1 Q' e: ]( o: a6 O3 H6 E
}
// Send the block to a subset of our peers
// 广播区块给部分peer% g2 V$ A9 G4 D
transfer := peers[:int(math.Sqrt(float64(len(peers))))]4 u' e, S7 j& m
for _, peer := range transfer {# J) j- s3 [+ P3 Q4 A
peer.AsyncSendNewBlock(block, td)
}
log.Trace("Propagated block", "hash", hash, "recipients", len(transfer), "duration", common.PrettyDuration(time.Since(block.ReceivedAt)))
return+ q6 { x0 f: x" ]. k. m q
}
// Otherwise if the block is indeed in out own chain, announce it6 U* r( M) a" X$ C0 g1 q! G
// 把区块hash值广播给所有peer
if pm.blockchain.HasBlock(hash, block.NumberU64()) {
for _, peer := range peers {( W! R: X8 T& v- |$ i; w+ k
peer.AsyncSendNewBlockHash(block)
}
log.Trace("Announced block", "hash", hash, "recipients", len(peers), "duration", common.PrettyDuration(time.Since(block.ReceivedAt)))1 m+ n2 ^; K$ l) x- g1 }/ A
}
}
peer.broadcase()是每个Peer连接的广播函数,它只广播3种消息:交易、完整的区块、区块的Hash,这样表明了节点只会主动广播这3中类型的数据,剩余的数据同步,都是通过请求-响应的方式。5 [+ Q+ e' \" e
// broadcast is a write loop that multiplexes block propagations, announcements
// and transaction broadcasts into the remote peer. The goal is to have an async t8 I% D# F6 H
// writer that does not lock up node internals.. L/ s) y8 [! R
func (p *peer) broadcast() {
for {2 x( t J% o4 `, s
select {2 j: S. ~% H9 A t+ P9 N
// 广播交易
case txs :=
Peer节点处理新区块
本节介绍远端节点收到2种区块同步消息的处理,其中NewBlockMsg的处理流程比较清晰,也简洁。NewBlockHashesMsg消息的处理就绕了2绕,从总体流程图1上能看出来,它需要先从给他发送消息Peer那里获取到完整的区块,剩下的流程和NewBlockMsg又一致了。
这部分涉及的模块多,画出来有种眼花缭乱的感觉,但只要抓住上面的主线,代码看起来还是很清晰的。通过图5先看下整体流程。
消息处理的起点是ProtocolManager.handleMsg,NewBlockMsg的处理流程是蓝色标记的区域,红色区域是单独的协程,是fetcher处理队列中区块的流程,如果从队列中取出的区块是当前链需要的,校验后,调用blockchian.InsertChain()把区块插入到区块链,最后写入数据库,这是黄色部分。最后,绿色部分是NewBlockHashesMsg的处理流程,代码流程上是比较复杂的,为了能通过图描述整体流程,我把它简化掉了。
仔细看看这幅图,掌握整体的流程后,接下来看每个步骤的细节。# N1 C$ ]6 p, [4 G# E, g
NewBlockMsg的处理0 Z0 E4 K& j7 K% H) F3 k
本节介绍节点收到完整区块的处理,流程如下:) w" N9 o2 {7 T# u( e' }# w0 f# I, R
首先进行RLP编解码,然后标记发送消息的Peer已经知道这个区块,这样本节点最后广播这个区块的Hash时,不会再发送给该Peer。( B/ N2 b) o5 D% ]
将区块存入到fetcher的队列,调用fetcher.Enqueue。
更新Peer的Head位置,然后判断本地链是否落后于Peer的链,如果是,则通过Peer更新本地链。
只看handle.Msg()的NewBlockMsg相关的部分。
case msg.Code == NewBlockMsg:' F, N- g) J2 A' k5 I4 Q
// Retrieve and decode the propagated block4 {% _ e" H. F9 Z8 A
// 收到新区块,解码,赋值接收数据
var request newBlockData( k. N' W9 U# j' B& t i$ D
if err := msg.Decode(&request); err != nil {6 Q6 h' Q) X4 y$ J3 W' P4 K! S1 V! D
return errResp(ErrDecode, "%v: %v", msg, err)
}
request.Block.ReceivedAt = msg.ReceivedAt
request.Block.ReceivedFrom = p
// Mark the peer as owning the block and schedule it for import
// 标记peer知道这个区块
p.MarkBlock(request.Block.Hash())! y- n& D8 h& O& c6 {# w
// 为啥要如队列?已经得到完整的区块了% J+ Y* O3 q+ g1 r
// 答:存入fetcher的优先级队列,fetcher会从队列中选取当前高度需要的块! H5 F, z8 q1 J3 a' E+ x0 m
pm.fetcher.Enqueue(p.id, request.Block)
// Assuming the block is importable by the peer, but possibly not yet done so,! [" f# d# K1 ^7 @ C
// calculate the head hash and TD that the peer truly must have.
// 截止到parent区块的头和难度
var (
trueHead = request.Block.ParentHash()
trueTD = new(big.Int).Sub(request.TD, request.Block.Difficulty())
)! q" k/ `6 o8 o% ]2 u8 r
// Update the peers total difficulty if better than the previous
// 如果收到的块的难度大于peer之前的,以及自己本地的,就去和这个peer同步# |& Z e2 g: W6 A
// 问题:就只用了一下块里的hash指,为啥不直接使用这个块呢,如果这个块不能用,干嘛不少发送些数据,减少网络负载呢。
// 答案:实际上,这个块加入到了优先级队列中,当fetcher的loop检查到当前下一个区块的高度,正是队列中有的,则不再向peer请求2 C0 @% P) N5 C! ]! d& k. B
// 该区块,而是直接使用该区块,检查无误后交给block chain执行insertChain6 U6 F0 X" _1 D; v" s- u6 L
if _, td := p.Head(); trueTD.Cmp(td) > 0 {& `9 B1 p; H4 n I9 G6 [
p.SetHead(trueHead, trueTD)
// Schedule a sync if above ours. Note, this will not fire a sync for a gap of
// a singe block (as the true TD is below the propagated block), however this
// scenario should easily be covered by the fetcher./ [5 V1 U$ o: D s- U5 N9 f3 N" ^
currentBlock := pm.blockchain.CurrentBlock()( k8 x% r* l) G h3 l! I! X$ J+ v3 o
if trueTD.Cmp(pm.blockchain.GetTd(currentBlock.Hash(), currentBlock.NumberU64())) > 0 { `6 I3 j v1 K0 R1 k
go pm.synchronise(p)6 |3 f1 Z$ |& x0 u: {
}8 v4 `3 D Z6 M. h; U& _
}
//------------------------ 以上 handleMsg, w( e$ }9 ~( [7 I6 A, a/ p
// Enqueue tries to fill gaps the the fetcher's future import queue.3 { [2 t& G8 U! a$ ~
// 发给inject通道,当前协程在handleMsg,通过通道发送给fetcher的协程处理
func (f *Fetcher) Enqueue(peer string, block *types.Block) error {
op := &inject{
origin: peer,: X# Q5 U( _4 p. x i/ J& @5 Y4 s
block: block,* h; [6 H) e5 Y0 w8 | e
}
select {( L; c* I! v, C% Q
case f.inject blockLimit {! R& j5 M/ a; r6 U4 G0 F
log.Debug("Discarded propagated block, exceeded allowance", "peer", peer, "number", block.Number(), "hash", hash, "limit", blockLimit)4 [( o6 x7 `' P/ E: z4 p
propBroadcastDOSMeter.Mark(1)
f.forgetHash(hash)2 u/ a) R a7 x: U% Q" a
return: F- V) O8 C+ O6 d' l" T
}
// Discard any past or too distant blocks
// 高度检查:未来太远的块丢弃& t# |4 d4 g8 M
if dist := int64(block.NumberU64()) - int64(f.chainHeight()); dist maxQueueDist {
log.Debug("Discarded propagated block, too far away", "peer", peer, "number", block.Number(), "hash", hash, "distance", dist) b# L0 e, X7 z' c) N5 Q- P: @5 B/ ?
propBroadcastDropMeter.Mark(1)! W) p1 ^) z7 T
f.forgetHash(hash)
return
}
// Schedule the block for future importing" S, d: [' n) ?2 c9 N
// 块先加入优先级队列,加入链之前,还有很多要做( o( P# {1 V* x- y# m0 P
if _, ok := f.queued[hash]; !ok {* d. s5 v. y1 v& G, T
op := &inject{" X! Y6 x9 y" C) R& b( D2 H/ C9 R
origin: peer,* u# Z$ U- m2 w" b1 ]
block: block,
}4 L' p( S+ `) i% l& ^; e* h2 T% ]2 O8 r- P
f.queues[peer] = count
f.queued[hash] = op
f.queue.Push(op, -float32(block.NumberU64())). M+ Z3 Z g! p
if f.queueChangeHook != nil {
f.queueChangeHook(op.block.Hash(), true)3 u7 E& w8 z3 R8 x4 p- u
}
log.Debug("Queued propagated block", "peer", peer, "number", block.Number(), "hash", hash, "queued", f.queue.Size())
}- N5 i' H8 ]; v% R
}
fetcher队列处理/ U! n% t' L7 [3 v7 ]7 ?
本节我们看看,区块加入队列后,fetcher如何处理区块,为何不直接校验区块,插入到本地链?
由于以太坊又Uncle的机制,节点可能收到老一点的一些区块。另外,节点可能由于网络原因,落后了几个区块,所以可能收到“未来”的一些区块,这些区块都不能直接插入到本地链。
区块入的队列是一个优先级队列,高度低的区块会被优先取出来。fetcher.loop是单独协程,不断运转,清理fecther中的事务和事件。首先会清理正在fetching的区块,但已经超时。然后处理优先级队列中的区块,判断高度是否是下一个区块,如果是则调用f.insert()函数,校验后调用BlockChain.InsertChain(),成功插入后,广播新区块的Hash。7 P8 i. }% b: i( W# k3 ^
// Loop is the main fetcher loop, checking and processing various notification
// events.
func (f *Fetcher) loop() {- r) U. c8 p- {
// Iterate the block fetching until a quit is requested2 z( w1 v) Q3 p
fetchTimer := time.NewTimer(0)+ b! Y- ^! Q3 }
completeTimer := time.NewTimer(0)- M+ d5 y1 |$ y9 t8 K8 ]
for {
// Clean up any expired block fetches& d y, Q; |( C0 H I
// 清理过期的区块# c" Q+ Y, X3 c& k! e9 f
for hash, announce := range f.fetching {
if time.Since(announce.time) > fetchTimeout {
f.forgetHash(hash)
}
}
// Import any queued blocks that could potentially fit7 m1 s; W( @& c b5 a
// 导入队列中合适的块+ F* z6 p' | t$ a) o4 I
height := f.chainHeight()" V" q5 R! [' b" F
for !f.queue.Empty() {3 ?0 _; K/ }: U9 ^2 t
op := f.queue.PopItem().(*inject)+ P3 N3 W. e: m/ g0 e: q: L
hash := op.block.Hash()
if f.queueChangeHook != nil {: L+ c3 w4 ~! e2 l* W
f.queueChangeHook(hash, false)
}
// If too high up the chain or phase, continue later: V# K1 s6 K/ U
// 块不是链需要的下一个块,再入优先级队列,停止循环
number := op.block.NumberU64()( c6 i6 | A0 M* x8 p" s; Y
if number > height+1 {
f.queue.Push(op, -float32(number))5 W( O0 Z3 K% \- G* _
if f.queueChangeHook != nil {6 s& G# T: B1 l$ z# `2 F3 A$ X
f.queueChangeHook(hash, true)
}
break& Z! _) {9 B3 `( }, b
}% s6 e$ E, C! v5 c3 [
// Otherwise if fresh and still unknown, try and import
// 高度正好是我们想要的,并且链上也没有这个块, v7 o7 ]' V/ V2 h
if number+maxUncleDist " M3 L3 D3 A8 X. T
func (f *Fetcher) insert(peer string, block *types.Block) {8 _9 u+ G) k, J+ x
hash := block.Hash()
// Run the import on a new thread. R* h0 j+ K7 Z4 b4 s+ z1 O
log.Debug("Importing propagated block", "peer", peer, "number", block.Number(), "hash", hash)
go func() {! b& }& g! {, O
defer func() { f.done & ^/ {5 d+ m; C a( y+ M
NewBlockHashesMsg的处理- |/ J9 m& ]% ` l; Y6 s9 B3 O
本节介绍NewBlockHashesMsg的处理,其实,消息处理是简单的,而复杂一点的是从Peer哪获取完整的区块,下节再看。
流程如下:
对消息进行RLP解码,然后标记Peer已经知道此区块。寻找出本地区块链不存在的区块Hash值,把这些未知的Hash通知给fetcher。fetcher.Notify记录好通知信息,塞入notify通道,以便交给fetcher的协程。fetcher.loop()会对notify中的消息进行处理,确认区块并非DOS攻击,然后检查区块的高度,判断该区块是否已经在fetching或者comleting(代表已经下载区块头,在下载body),如果都没有,则加入到announced中,触发0s定时器,进行处理。
关于announced下节再介绍。8 a2 L0 P& m- V
// handleMsg()部分' t5 B: F% X3 y2 E3 f+ d
case msg.Code == NewBlockHashesMsg:9 C& T5 w& X# K
var announces newBlockHashesData& \$ M) {# k' J6 T. s0 f
if err := msg.Decode(&announces); err != nil { C% D9 C+ D/ h# K* j
return errResp(ErrDecode, "%v: %v", msg, err)
}( S' F; }6 Y) [' x7 e+ P+ Y
// Mark the hashes as present at the remote node
for _, block := range announces {7 M) H; {9 d/ g2 T
p.MarkBlock(block.Hash): h: ?; {& N! z' a
}9 o+ M- Y+ M/ c7 q9 S
// Schedule all the unknown hashes for retrieval/ l9 z- @5 j e+ v& z% x
// 把本地链没有的块hash找出来,交给fetcher去下载
unknown := make(newBlockHashesData, 0, len(announces))
for _, block := range announces {
if !pm.blockchain.HasBlock(block.Hash, block.Number) {
unknown = append(unknown, block)
}6 y: ^2 Z6 \6 J! C& {/ i
}
for _, block := range unknown {
pm.fetcher.Notify(p.id, block.Hash, block.Number, time.Now(), p.RequestOneHeader, p.RequestBodies)
}- Y' t' k$ Z" h3 O& _# k& e
// Notify announces the fetcher of the potential availability of a new block in
// the network.
// 通知fetcher(自己)有新块产生,没有块实体,有hash、高度等信息
func (f *Fetcher) Notify(peer string, hash common.Hash, number uint64, time time.Time, a9 b" p' y/ g6 a1 J B
headerFetcher headerRequesterFn, bodyFetcher bodyRequesterFn) error {
block := &announce{+ I8 C6 \; v( A' j
hash: hash,4 h1 W# ]8 V! _& @0 D8 I% o
number: number,
time: time,7 D) O) r, `4 b5 w# \2 I
origin: peer,
fetchHeader: headerFetcher,
fetchBodies: bodyFetcher,
}
select {7 C* C* ^" }5 E- ?; Y$ N3 {
case f.notify hashLimit {
log.Debug("Peer exceeded outstanding announces", "peer", notification.origin, "limit", hashLimit)
propAnnounceDOSMeter.Mark(1)3 L1 t( t( _: Z" |, V9 _
break
}; e2 R* B+ M! Z3 V. l: u9 ~2 A, q1 H1 B
// If we have a valid block number, check that it's potentially useful! R; F% f& A0 U0 u, f
// 高度检查% i+ E1 X+ D( G1 i
if notification.number > 0 {2 p7 G4 Z) Y0 ?+ ^
if dist := int64(notification.number) - int64(f.chainHeight()); dist maxQueueDist {5 u* i, ?0 ^+ J# s/ W
log.Debug("Peer discarded announcement", "peer", notification.origin, "number", notification.number, "hash", notification.hash, "distance", dist)
propAnnounceDropMeter.Mark(1)
break5 w' a9 f' m# {( y, c
}6 L- G7 e( V' n5 j+ y$ V. ~9 R9 O
}
// All is well, schedule the announce if block's not yet downloading: o- @+ \! A- m+ v0 P* {
// 检查是否已经在下载,已下载则忽略
if _, ok := f.fetching[notification.hash]; ok {
break. e( E+ a% Q3 N, c
}
if _, ok := f.completing[notification.hash]; ok {4 U" w; Y1 {' O5 R0 `# G2 A+ l/ z
break7 {/ D8 Y0 Y( r1 \, c' S
}& Q6 }3 h6 q. v0 P+ x7 J5 U; t
// 更新peer已经通知给我们的区块数量
f.announces[notification.origin] = count
// 把通知信息加入到announced,供调度
f.announced[notification.hash] = append(f.announced[notification.hash], notification)
if f.announceChangeHook != nil && len(f.announced[notification.hash]) == 1 {
f.announceChangeHook(notification.hash, true)
}
if len(f.announced) == 1 {3 D% y8 C! N9 m) V
// 有通知放入到announced,则重设0s定时器,loop的另外一个分支会处理这些通知' e0 E' @; q! Z4 C" w# C& ~# A
f.rescheduleFetch(fetchTimer)* o) E6 r% l5 w' B6 i
}+ z5 i. i( k* V% T7 R. r: j$ c
fetcher获取完整区块
本节介绍fetcher获取完整区块的过程,这也是fetcher最重要的功能,会涉及到fetcher至少80%的代码。单独拉放一大节吧。. ?+ }1 l r$ L B# f
Fetcher的大头( N0 j, x5 ` @/ ~6 ]+ o4 W8 c
Fetcher最主要的功能就是获取完整的区块,然后在合适的实际交给InsertChain去验证和插入到本地区块链。我们还是从宏观入手,看Fetcher是如何工作的,一定要先掌握好宏观,因为代码层面上没有这么清晰。4 J) J" E m T, Y7 W/ T; h
宏观
首先,看两个节点是如何交互,获取完整区块,使用时序图的方式看一下,见图6,流程很清晰不再文字介绍。- G2 U0 u" V7 `; {/ R/ U: Y& A
再看下获取区块过程中,fetcher内部的状态转移,它使用状态来记录,要获取的区块在什么阶段,见图7。我稍微解释一下:
收到NewBlockHashesMsg后,相关信息会记录到announced,进入announced状态,代表了本节点接收了消息。announced由fetcher协程处理,经过校验后,会向给他发送消息的Peer发送请求,请求该区块的区块头,然后进入fetching状态。获取区块头后,如果区块头表示没有交易和uncle,则转移到completing状态,并且使用区块头合成完整的区块,加入到queued优先级队列。获取区块头后,如果区块头表示该区块有交易和uncle,则转移到fetched状态,然后发送请求,请求交易和uncle,然后转移到completing状态。收到交易和uncle后,使用头、交易、uncle这3个信息,生成完整的区块,加入到队列queued。
微观5 b. K' _7 x) P: U8 K5 O7 Y7 I
接下来就是从代码角度看如何获取完整区块的流程了,有点多,看不懂的时候,再回顾下上面宏观的介绍图。* s' w% g5 y) y+ ]0 S. R: E$ ?, w6 \
首先看Fetcher的定义,它存放了通信数据和状态管理,捡加注释的看,上文提到的状态,里面都有。" e" Z* ~5 s0 U0 u
// Fetcher is responsible for accumulating block announcements from various peers" x0 A5 g2 g9 p3 H, P0 g0 S
// and scheduling them for retrieval.0 V! U. x& g# Q5 j* o, f; l
// 积累块通知,然后调度获取这些块
type Fetcher struct {
// Various event channels
// 收到区块hash值的通道
notify chan *announce; b' x6 H, @& |0 d( R0 e7 r3 T3 r
// 收到完整区块的通道
inject chan *inject
blockFilter chan chan []*types.Block
// 过滤header的通道的通道) Z# p6 k" R8 h6 i- b9 C. k/ S* Y- i
headerFilter chan chan *headerFilterTask
// 过滤body的通道的通道
bodyFilter chan chan *bodyFilterTask9 U5 R' {+ ~4 T: K4 U3 J
done chan common.Hash/ x# h: Z0 A- }5 J! X8 A- U
quit chan struct{}
// Announce states
// Peer已经给了本节点多少区块头通知+ R3 e- h; m4 ?6 T
announces map[string]int // Per peer announce counts to prevent memory exhaustion' |+ \ F8 _, U
// 已经announced的区块列表
announced map[common.Hash][]*announce // Announced blocks, scheduled for fetching
// 正在fetching区块头的请求4 @. n! d2 ?# s$ d
fetching map[common.Hash]*announce // Announced blocks, currently fetching
// 已经fetch到区块头,还差body的请求,用来获取body
fetched map[common.Hash][]*announce // Blocks with headers fetched, scheduled for body retrieval1 |4 p% r/ u% K& n$ N6 i
// 已经得到区块头的
completing map[common.Hash]*announce // Blocks with headers, currently body-completing
// Block cache' e, S l' s& W$ ^+ E8 n$ S
// queue,优先级队列,高度做优先级3 A ]) `% V3 |2 L4 I+ Z- k4 y& b
// queues,统计peer通告了多少块0 _" ]3 r) `6 N! S9 q* R
// queued,代表这个块如队列了,. a! O" o* B. ~# [2 o e8 u
queue *prque.Prque // Queue containing the import operations (block number sorted). [& c* V* I+ H9 r
queues map[string]int // Per peer block counts to prevent memory exhaustion# L; k2 r$ Z6 c& I7 @: Y% ~# T
queued map[common.Hash]*inject // Set of already queued blocks (to dedupe imports)
// Callbacks) g' p( x5 i7 Y
getBlock blockRetrievalFn // Retrieves a block from the local chain9 R, ? A5 s) v# j) m* y# A5 D5 T$ q
verifyHeader headerVerifierFn // Checks if a block's headers have a valid proof of work,验证区块头,包含了PoW验证
broadcastBlock blockBroadcasterFn // Broadcasts a block to connected peers,广播给peer
chainHeight chainHeightFn // Retrieves the current chain's height% n: W$ v D+ u+ t
insertChain chainInsertFn // Injects a batch of blocks into the chain,插入区块到链的函数
dropPeer peerDropFn // Drops a peer for misbehaving4 g+ w9 e0 q ~
// Testing hooks
announceChangeHook func(common.Hash, bool) // Method to call upon adding or deleting a hash from the announce list
queueChangeHook func(common.Hash, bool) // Method to call upon adding or deleting a block from the import queue% G; z- ^1 p; s
fetchingHook func([]common.Hash) // Method to call upon starting a block (eth/61) or header (eth/62) fetch
completingHook func([]common.Hash) // Method to call upon starting a block body fetch (eth/62)
importedHook func(*types.Block) // Method to call upon successful block import (both eth/61 and eth/62)( Q- a4 J( ~. s' f% \/ A8 c3 B9 G9 e
}* M4 Q- ]* G0 Q4 ]! ?
NewBlockHashesMsg消息的处理前面的小节已经讲过了,不记得可向前翻看。这里从announced的状态处理说起。loop() 中,fetchTimer超时后,代表了收到了消息通知,需要处理,会从announced中选择出需要处理的通知,然后创建请求,请求区块头,由于可能有很多节点都通知了它某个区块的Hash,所以随机的从这些发送消息的Peer中选择一个Peer,发送请求的时候,为每个Peer都创建了单独的协程。
case arriveTimeout-gatherSlack {: `' E7 O+ R0 |$ U- L
// Pick a random peer to retrieve from, reset all others
// 可能有很多peer都发送了这个区块的hash值,随机选择一个peer5 A5 P. m/ h' i- o, G
announce := announces[rand.Intn(len(announces))]
f.forgetHash(hash)
// If the block still didn't arrive, queue for fetching
// 本地还没有这个区块,创建获取区块的请求
if f.getBlock(hash) == nil {
request[announce.origin] = append(request[announce.origin], hash)
f.fetching[hash] = announce
}4 @; T8 t* q( _2 @
}
}
// Send out all block header requests' H4 G% Y! M, k0 [; }* k
// 把所有的request发送出去5 q: c8 U8 a, K! Z5 e5 ^0 Y1 G/ j3 }
// 为每一个peer都创建一个协程,然后请求所有需要从该peer获取的请求8 v+ a# O3 k1 x8 A. V
for peer, hashes := range request {7 P& y0 I- H& N5 m9 t, f
log.Trace("Fetching scheduled headers", "peer", peer, "list", hashes)& F! ~# U5 J4 k3 o% m6 U! x
// Create a closure of the fetch and schedule in on a new thread* j2 f% O V/ F6 s* l
fetchHeader, hashes := f.fetching[hashes[0]].fetchHeader, hashes
go func() {
if f.fetchingHook != nil {( Q) o8 c; u$ j2 w2 Z# k
f.fetchingHook(hashes)
}
for _, hash := range hashes {( P: M" z7 O/ Z! Q, _3 s
headerFetchMeter.Mark(1)
fetchHeader(hash) // Suboptimal, but protocol doesn't allow batch header retrievals* t0 M2 c' ?+ Q
}0 t p, R3 l: g' L: W7 n3 \. U
}()
}+ Y/ X8 u& p# T! {
// Schedule the next fetch if blocks are still pending
f.rescheduleFetch(fetchTimer): m$ t+ F0 a5 ` ]! O
从Notify的调用中,可以看出,fetcherHeader()的实际函数是RequestOneHeader(),该函数使用的消息是GetBlockHeadersMsg,可以用来请求多个区块头,不过fetcher只请求一个。
pm.fetcher.Notify(p.id, block.Hash, block.Number, time.Now(), p.RequestOneHeader, p.RequestBodies)2 X$ T! M: ~7 D1 a
// RequestOneHeader is a wrapper around the header query functions to fetch a
// single header. It is used solely by the fetcher.; E' @! O' X# Y' z* c7 ]+ q
func (p *peer) RequestOneHeader(hash common.Hash) error {
p.Log().Debug("Fetching single header", "hash", hash)
return p2p.Send(p.rw, GetBlockHeadersMsg, &getBlockHeadersData{Origin: hashOrNumber{Hash: hash}, Amount: uint64(1), Skip: uint64(0), Reverse: false})
}
GetBlockHeadersMsg的处理如下:因为它是获取多个区块头的,所以处理起来比较“麻烦”,还好,fetcher只获取一个区块头,其处理在20行~33行,获取下一个区块头的处理逻辑,这里就不看了,最后调用SendBlockHeaders()将区块头发送给请求的节点,消息是BlockHeadersMsg。
···
// handleMsg()
// Block header query, collect the requested headers and reply
case msg.Code == GetBlockHeadersMsg:$ W4 ?+ |7 a9 Q( N6 |- n1 Z
// Decode the complex header query& v+ T R. i% X0 d
var query getBlockHeadersData
if err := msg.Decode(&query); err != nil {7 Q# w; n5 H7 w7 I% U
return errResp(ErrDecode, “%v: %v”, msg, err)/ d: P5 W/ R8 t* V% J" r6 p/ p
}+ k" L6 G# u3 y; q
hashMode := query.Origin.Hash != (common.Hash{})7 s, x: e5 h7 N5 b+ ]( f
// Gather headers until the fetch or network limits is reached
// 收集区块头,直到达到限制9 n$ C8 W+ N N5 q1 G6 s* R
var (3 T) |) s6 N0 S p
bytes common.StorageSize3 o# P1 a1 q8 ?* G2 c4 c H" b$ I
headers []*types.Header0 X$ \% e0 `: a1 o
unknown bool5 D% y2 y5 @& x) K9 d
)
// 自己已知区块 && 少于查询的数量 && 大小小于2MB && 小于能下载的最大数量2 B( F% ~3 w4 F! _3 O
for !unknown && len(headers)
`BlockHeadersMsg`的处理很有意思,因为`GetBlockHeadersMsg`并不是fetcher独占的消息,downloader也可以调用,所以,响应消息的处理需要分辨出是fetcher请求的,还是downloader请求的。它的处理逻辑是:fetcher先过滤收到的区块头,如果fetcher不要的,那就是downloader的,在调用`fetcher.FilterHeaders`的时候,fetcher就将自己要的区块头拿走了。
// handleMsg()
case msg.Code == BlockHeadersMsg:
// A batch of headers arrived to one of our previous requests! F+ c I5 J/ Z# o
var headers []*types.Header+ X2 V0 _' ] c, b+ @8 @4 E
if err := msg.Decode(&headers); err != nil {8 o" y' E% M+ m/ i7 h0 |! u
return errResp(ErrDecode, “msg %v: %v”, msg, err)
}
// If no headers were received, but we’re expending a DAO fork check, maybe it’s that& z( W6 L8 N( }! |$ B) M6 f' I
// 检查是不是当前DAO的硬分叉
if len(headers) == 0 && p.forkDrop != nil {, v# W2 Y5 Z3 C
// Possibly an empty reply to the fork header checks, sanity check TDs: m. J/ r; ~! s; \- N. l+ D8 h) L
verifyDAO := true/ p* o# z p; C0 |
// If we already have a DAO header, we can check the peer's TD against it. If, x0 |6 Z( @$ |3 r% ]/ a1 \- V1 d
// the peer's ahead of this, it too must have a reply to the DAO check
if daoHeader := pm.blockchain.GetHeaderByNumber(pm.chainconfig.DAOForkBlock.Uint64()); daoHeader != nil {- u7 P$ B. P, H5 G4 S& z) K& Z4 [
if _, td := p.Head(); td.Cmp(pm.blockchain.GetTd(daoHeader.Hash(), daoHeader.Number.Uint64())) >= 0 {& ^9 i8 |/ t7 g+ R4 u
verifyDAO = false( O" H+ m- d$ E. H' _
}3 o5 U3 B' i3 c! E0 r6 w
}# ~2 N- t. w% h0 o# i- o# a% o
// If we're seemingly on the same chain, disable the drop timer4 F1 E* B8 P( `$ G/ ?7 e
if verifyDAO {4 B' E' g5 L5 M& @) E
p.Log().Debug("Seems to be on the same side of the DAO fork")
p.forkDrop.Stop()2 [$ n! [+ ?, l. c* K2 K5 [
p.forkDrop = nil
return nil( K. m% ^ ~: l2 g" L6 z' \+ j
}
}' h! Z" C4 H! S
// Filter out any explicitly requested headers, deliver the rest to the downloader! L& f; t+ j' s( U2 M
// 过滤是不是fetcher请求的区块头,去掉fetcher请求的区块头再交给downloader3 w3 j. t" f. [/ a3 y1 b7 W
filter := len(headers) == 1( e' a. |% ]2 B! s& h5 A! m: b' h
if filter {& Y4 d5 H* Y1 @4 u2 o7 a! z/ \* {, g2 e9 h
// If it's a potential DAO fork check, validate against the rules4 f( k7 k5 ^! x2 M
// 检查是否硬分叉
if p.forkDrop != nil && pm.chainconfig.DAOForkBlock.Cmp(headers[0].Number) == 0 {6 i7 U m' L% f) ]% [
// Disable the fork drop timer
p.forkDrop.Stop()
p.forkDrop = nil2 R! m0 X9 s& @) c5 K8 o% [
// Validate the header and either drop the peer or continue
if err := misc.VerifyDAOHeaderExtraData(pm.chainconfig, headers[0]); err != nil {) n9 i% M+ ^1 F( {/ N
p.Log().Debug("Verified to be on the other side of the DAO fork, dropping")4 ^2 W; c/ D4 f% K' o# |
return err5 ^- S! ^% H# X9 w9 a4 d" @5 O
}0 t6 i7 K5 x o1 R' q% @
p.Log().Debug("Verified to be on the same side of the DAO fork")1 t+ S$ M) z2 U% y$ z( R) Q
return nil% Y2 X$ ^* d" v; B0 w
}+ I# R, ^$ L/ O( ?+ o
// Irrelevant of the fork checks, send the header to the fetcher just in case9 S2 U& c* C. B, l3 J
// 使用fetcher过滤区块头
headers = pm.fetcher.FilterHeaders(p.id, headers, time.Now())
}
// 剩下的区块头交给downloader9 S4 E( v9 l* C8 i. U
if len(headers) > 0 || !filter {. E/ Z+ r2 H5 {3 n, l) D6 U
err := pm.downloader.DeliverHeaders(p.id, headers)
if err != nil {
log.Debug("Failed to deliver headers", "err", err)
}$ |& q5 E* B) J
}
`FilterHeaders()`是一个很有大智慧的函数,看起来耐人寻味,但实在妙。它要把所有的区块头,都传递给fetcher协程,还要获取fetcher协程处理后的结果。`fetcher.headerFilter`是存放通道的通道,而`filter`是存放包含区块头过滤任务的通道。它先把`filter`传递给了`headerFilter`,这样`fetcher`协程就在另外一段等待了,而后将`headerFilterTask`传入`filter`,`fetcher`就能读到数据了,处理后,再将数据写回`filter`而刚好被`FilterHeaders`函数处理了,该函数实际运行在`handleMsg()`的协程中。
每个Peer都会分配一个ProtocolManager然后处理该Peer的消息,但`fetcher`只有一个事件处理协程,如果不创建一个`filter`,fetcher哪知道是谁发给它的区块头呢?过滤之后,该如何发回去呢?
// FilterHeaders extracts all the headers that were explicitly requested by the fetcher,2 C8 O- i5 H" u2 o$ S8 A6 b% t2 a [
// returning those that should be handled differently.3 n7 b0 l, L0 k5 A" c
// 寻找出fetcher请求的区块头
func (f *Fetcher) FilterHeaders(peer string, headers []*types.Header, time time.Time) []*types.Header {- H) y/ Q8 U- s5 v J+ E8 H
log.Trace(“Filtering headers”, “peer”, peer, “headers”, len(headers))
// Send the filter channel to the fetcher. N+ h8 p% }- b$ A8 C* o
// 任务通道
filter := make(chan *headerFilterTask)
select {, J1 \& [! j( @3 X
// 任务通道发送到这个通道
case f.headerFilter
}8 [1 |) ^- `7 r ]6 C6 M3 d$ m
接下来要看f.headerFilter的处理,这段代码有90行,它做了一下几件事:$ W1 W5 l0 }9 p4 G
1. 从`f.headerFilter`取出`filter`,然后取出过滤任务`task`。
2. 它把区块头分成3类:`unknown`这不是分是要返回给调用者的,即`handleMsg()`, `incomplete`存放还需要获取body的区块头,`complete`存放只包含区块头的区块。遍历所有的区块头,填到到对应的分类中,具体的判断可看18行的注释,记住宏观中将的状态转移图。: Z9 A3 |" Q3 B& O# _* z
3. 把`unknonw`中的区块返回给`handleMsg()`。: d( |- h2 O8 C s( F0 F
4. 把` incomplete`的区块头获取状态移动到`fetched`状态,然后触发定时器,以便去处理complete的区块。2 B/ X( I0 U3 r
5. 把`compelete`的区块加入到`queued`。* f' M) a; Y# {& S
// fetcher.loop()2 P" Q$ d' j$ j7 W6 S
case filter := , U4 B' P) n/ I. e& U; |6 }
// Split the batch of headers into unknown ones (to return to the caller),
// known incomplete ones (requiring body retrievals) and completed blocks.- _5 ? g8 }+ i7 C
// unknown的不是fetcher请求的,complete放没有交易和uncle的区块,有头就够了,incomplete放
// 还需要获取uncle和交易的区块
unknown, incomplete, complete := []*types.Header{}, []*announce{}, []*types.Block{}2 e6 @0 L6 e) F8 _; e
// 遍历所有收到的header9 S. n% [" g! T& u- r
for _, header := range task.headers {0 R$ @+ r( @9 T7 ]
hash := header.Hash()
// Filter fetcher-requested headers from other synchronisation algorithms
// 是正在获取的hash,并且对应请求的peer,并且未fetched,未completing,未queued
if announce := f.fetching[hash]; announce != nil && announce.origin == task.peer && f.fetched[hash] == nil && f.completing[hash] == nil && f.queued[hash] == nil {
// If the delivered header does not match the promised number, drop the announcer
// 高度校验,竟然不匹配,扰乱秩序,peer肯定是坏蛋。3 C( x, d1 b( X9 C: T1 A# B
if header.Number.Uint64() != announce.number {2 F; k' K3 ~4 \) G% U( c" v( K
log.Trace("Invalid block number fetched", "peer", announce.origin, "hash", header.Hash(), "announced", announce.number, "provided", header.Number)
f.dropPeer(announce.origin)
f.forgetHash(hash)1 J2 u: u5 i6 m0 A# e2 ]! B
continue9 n0 r5 U2 f% W7 x) F9 [( s( I
}
// Only keep if not imported by other means
// 本地链没有当前区块
if f.getBlock(hash) == nil {& c& z, R: e: {+ F# X6 N
announce.header = header5 K, \* W+ e1 X- d, k
announce.time = task.time
// If the block is empty (header only), short circuit into the final import queue
// 如果区块没有交易和uncle,加入到complete' K2 `7 Y# _- E+ e
if header.TxHash == types.DeriveSha(types.Transactions{}) && header.UncleHash == types.CalcUncleHash([]*types.Header{}) {; N4 o* L8 |, u
log.Trace("Block empty, skipping body retrieval", "peer", announce.origin, "number", header.Number, "hash", header.Hash())
block := types.NewBlockWithHeader(header)
block.ReceivedAt = task.time1 J T# P- }2 M# a% D% ~( h$ \
complete = append(complete, block), Z2 o2 Y: d Y z6 f1 U2 |+ R7 H
f.completing[hash] = announce
continue4 E4 b9 }4 N& Y- s8 t
}" g' n. ^' B' ?; a; }
// Otherwise add to the list of blocks needing completion1 v( n/ D) z9 A, l( F0 M( j, D
// 否则就是不完整的区块) w4 v$ C" {% k+ Y& |; h2 n
incomplete = append(incomplete, announce)
} else {
log.Trace("Block already imported, discarding header", "peer", announce.origin, "number", header.Number, "hash", header.Hash()): a: b8 i' G8 d% K
f.forgetHash(hash)
}
} else {3 b. e. |, o+ D6 D3 f9 m. u
// Fetcher doesn't know about it, add to the return list
// 没请求过的header1 w# E: p4 l% |' t" |
unknown = append(unknown, header)
}" B" d! g& O5 w( z
}4 G" H& @' l+ R7 O
// 把未知的区块头,再传递会filter
headerFilterOutMeter.Mark(int64(len(unknown)))
select {: F( ~" w. _0 v3 |1 c! g6 g
case filter / j* v3 H- x- k$ M( _/ T6 n
跟随状态图的转义,剩下的工作是`fetched`转移到`completing` ,上面的流程已经触发了`completeTimer`定时器,超时后就会处理,流程与请求Header类似,不再赘述,此时发送的请求消息是`GetBlockBodiesMsg`,实际调的函数是`RequestBodies`。
// fetcher.loop()
case
// 遍历所有待获取body的announce9 D3 v7 N6 b, ?+ F, y0 u8 B, h
for hash, announces := range f.fetched {8 e2 q8 C! Y7 ]) F9 n: p% D8 |2 `
// Pick a random peer to retrieve from, reset all others( U9 ^ Y' a# \% \4 g- x/ h
// 随机选一个Peer发送请求,因为可能已经有很多Peer通知它这个区块了8 d) u$ Y5 @1 h; Q) O5 ~( a9 i, U
announce := announces[rand.Intn(len(announces))]. D. Q/ X" t2 n2 o
f.forgetHash(hash)
// If the block still didn't arrive, queue for completion9 s. w$ e6 L2 o1 @8 N/ l2 R
// 如果本地没有这个区块,则放入到completing,创建请求
if f.getBlock(hash) == nil {
request[announce.origin] = append(request[announce.origin], hash)
f.completing[hash] = announce/ n) X G" p( W* i+ m/ L
}$ M, D' l* ~1 F3 a% _0 a
}* Z- }- a4 V8 J; ?1 J' _- E; Q" `, L9 i Q9 O
// Send out all block body requests, X6 V( j" y7 Q* S
// 发送所有的请求,获取body,依然是每个peer一个单独协程: u. ?5 Q: a+ d1 q
for peer, hashes := range request {" S+ d* |; r2 k3 j0 C3 l
log.Trace("Fetching scheduled bodies", "peer", peer, "list", hashes); L0 T5 H2 i5 }. @, w
// Create a closure of the fetch and schedule in on a new thread/ j( b. Z5 w: p1 Z' n& k* Q
if f.completingHook != nil {
f.completingHook(hashes)( F! J1 O3 R; k, N! ?# @$ O% O
}
bodyFetchMeter.Mark(int64(len(hashes))). M& @7 _9 t4 I9 H& ?
go f.completing[hashes[0]].fetchBodies(hashes)$ A0 u! S& i$ A+ _+ A
}
// Schedule the next fetch if blocks are still pending
f.rescheduleComplete(completeTimer): a: O8 }- X7 j4 r6 a
`handleMsg()`处理该消息也是干净利落,直接获取RLP格式的body,然后发送响应消息。
// handleMsg()* C' r$ e" K; S0 Z" V
case msg.Code == GetBlockBodiesMsg:9 E [8 q5 A6 E
// Decode the retrieval message; {( @% a/ Z0 M! K
msgStream := rlp.NewStream(msg.Payload, uint64(msg.Size))
if _, err := msgStream.List(); err != nil {$ {' o8 j2 Y+ \
return err
}
// Gather blocks until the fetch or network limits is reached/ | |& @* @& u" F
var (- }' m- d) Z1 e0 e K
hash common.Hash0 A7 x, N) Z* E; E H" V
bytes int
bodies []rlp.RawValue! I, c; @7 @) Q' H2 \8 f, f
)
// 遍历所有请求- b& ?6 N! D, G" b+ k/ M
for bytes
响应消息`BlockBodiesMsg`的处理与处理获取header的处理原理相同,先交给fetcher过滤,然后剩下的才是downloader的。需要注意一点,响应消息里只包含交易列表和叔块列表。0 E* } M+ |9 w/ ?
// handleMsg(); d3 ]* s$ N9 E" E7 e, T
case msg.Code == BlockBodiesMsg:$ Q9 ~$ O' r# c$ o- x! i! V
// A batch of block bodies arrived to one of our previous requests
var request blockBodiesData
if err := msg.Decode(&request); err != nil {& G {. J4 B- m4 N
return errResp(ErrDecode, “msg %v: %v”, msg, err)/ ~2 Y1 t/ b- E: m9 M* v6 s, r
}/ k" e8 R. T# ^7 U
// Deliver them all to the downloader for queuing
// 传递给downloader去处理
transactions := make([][]*types.Transaction, len(request))
uncles := make([][]*types.Header, len(request))# m, B! J) P: C" Z3 k
for i, body := range request {
transactions = body.Transactions8 [: K0 w6 C) B) [& o6 [" p
uncles = body.Uncles
}
// Filter out any explicitly requested bodies, deliver the rest to the downloader$ J7 t7 {5 m W
// 先让fetcher过滤去fetcher请求的body,剩下的给downloader0 P5 H7 K# ~4 C, W2 ?0 D
filter := len(transactions) > 0 || len(uncles) > 0
if filter {
transactions, uncles = pm.fetcher.FilterBodies(p.id, transactions, uncles, time.Now())8 I8 R+ x; h9 n% @; |' T3 K/ Z
}$ w- w# s e6 ]: {
// 剩下的body交给downloader
if len(transactions) > 0 || len(uncles) > 0 || !filter {* ?) Z$ g7 b: r1 a0 f
err := pm.downloader.DeliverBodies(p.id, transactions, uncles)& d. H7 _6 }( @0 V5 s) A
if err != nil {, }: g2 o) i7 Z Y1 U0 n
log.Debug("Failed to deliver bodies", "err", err)1 r6 w0 m0 N5 `- x2 d4 M
}- a' q4 O& d& J& v' O- L4 ^
}
过滤函数的原理也与Header相同。
// FilterBodies extracts all the block bodies that were explicitly requested by6 k+ X1 U; W& ]# v: A3 j
// the fetcher, returning those that should be handled differently.
// 过去出fetcher请求的body,返回它没有处理的,过程类型header的处理" d$ {- Y, p( K+ n: I2 p
func (f *Fetcher) FilterBodies(peer string, transactions [][]*types.Transaction, uncles [][]*types.Header, time time.Time) ([][]*types.Transaction, [][]*types.Header) {
log.Trace(“Filtering bodies”, “peer”, peer, “txs”, len(transactions), “uncles”, len(uncles))
// Send the filter channel to the fetcher
filter := make(chan *bodyFilterTask)
select {, M! m1 B0 x# a
case f.bodyFilter ; e# j7 E, _2 X& h8 ~
}& D" x2 |& W5 K E
实际过滤body的处理瞧一下,这和Header的处理是不同的。直接看不点:6 z# l" y' B* R
1. 它要的区块,单独取出来存到`blocks`中,它不要的继续留在`task`中。& p$ c E5 `" O: X8 J
2. 判断是不是fetcher请求的方法:如果交易列表和叔块列表计算出的hash值与区块头中的一样,并且消息来自请求的Peer,则就是fetcher请求的。
3. 将`blocks`中的区块加入到`queued`,终结。
case filter :=
blocks := []*types.Block{}
// 获取的每个body的txs列表和uncle列表
// 遍历每个区块的txs列表和uncle列表,计算hash后判断是否是当前fetcher请求的body
for i := 0; i : t! p) e2 o0 Q! o$ d
} R {: ` y& Y% i1 `! F- p) I
, I( [1 V/ {: `9 |4 i8 c$ h
至此,fetcher获取完整区块的流程讲完了,fetcher模块中80%的代码也都贴出来了,还有2个值得看看的函数:
1. `forgetHash(hash common.Hash)`:用于清空指定hash指的记/状态录信息。% W7 C0 }/ `& y( X! p7 t9 W
2. `forgetBlock(hash common.Hash)`:用于从队列中移除一个区块。
最后了,再回到开始看看fetcher模块和新区块的传播流程,有没有豁然开朗。
成为第一个吐槽的人